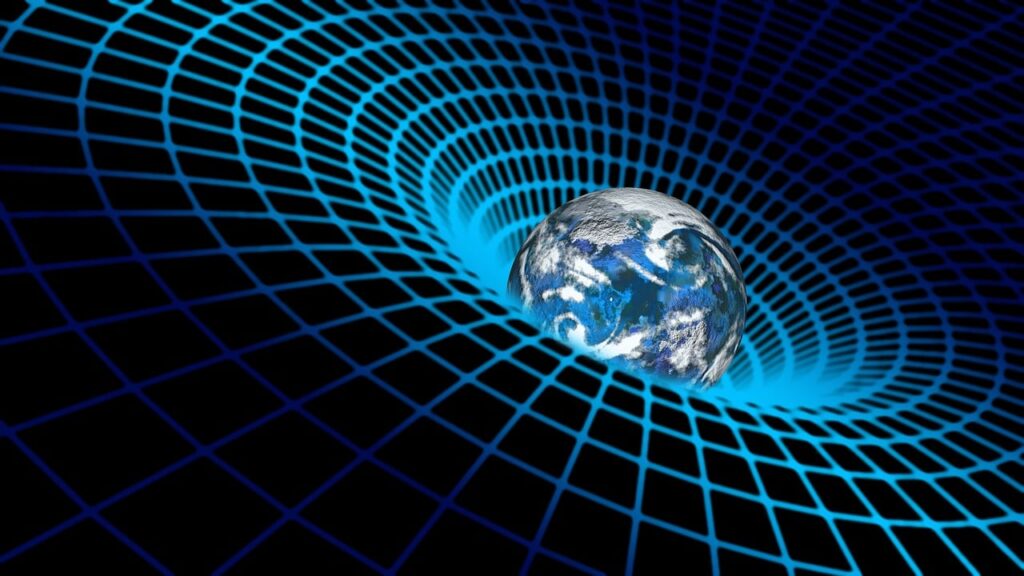
Proposed by Albert Einstein in 1915, the Theory of General Relativity (GR) extends Special Relativity to include gravity. It describes how massive objects warp space and time, fundamentally changing our understanding of gravity.
Key Principles of General Relativity
-
Equivalence Principle:
- Acceleration and gravity are indistinguishable from each other.
- A person inside a sealed spaceship cannot tell whether they are in deep space accelerating or standing on Earth’s surface under gravity.
-
Gravity as Curvature of Spacetime:
- Instead of Newton’s idea of gravity as a force, Einstein showed that mass bends space and time, and objects follow the curved paths (geodesics) created by this warping.
- More massive objects create stronger curvature, affecting the motion of nearby objects.
Key Predictions and Effects of General Relativity
-
Time Dilation in Gravity (Gravitational Time Dilation):
- Clocks run slower in strong gravitational fields.
- Example: Time moves slightly slower on Earth’s surface compared to a satellite in orbit (confirmed by GPS systems).
-
Bending of Light (Gravitational Lensing):
- Light bends when passing near massive objects due to spacetime curvature.
- Observed during a solar eclipse in 1919, confirming Einstein’s theory.
-
Black Holes:
- Regions where gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape.
- Predicted by Einstein’s equations and confirmed by observations of black hole mergers.
-
Expansion of the Universe:
- Einstein’s equations predicted an expanding or contracting universe, later confirmed by Edwin Hubble’s discovery of the expanding universe.
-
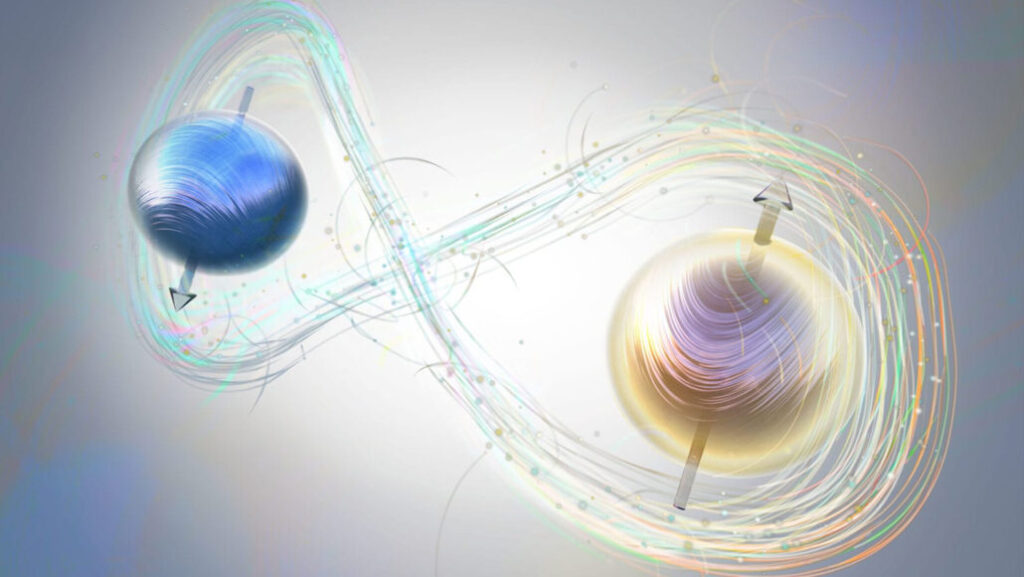
Gravitational Waves:
- Ripples in spacetime caused by massive accelerating objects (e.g., merging black holes).
- First detected in 2015 by LIGO, confirming Einstein’s prediction.
Mathematical Foundation:
The core equation of General Relativity is Einstein’s Field Equation:
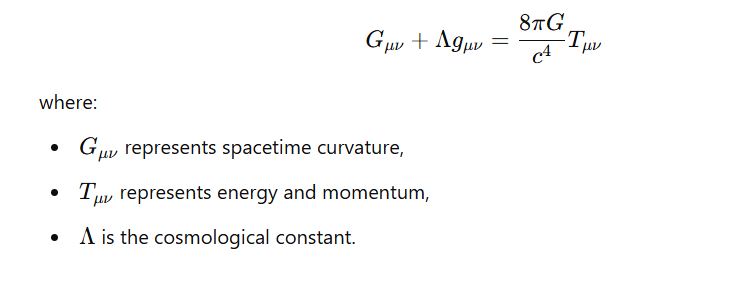
Experimental Proofs of General Relativity:
✔ 1919 Solar Eclipse: Light bending observed around the Sun.
✔ GPS Systems: Time correction due to gravitational time dilation.
✔ Gravitational Waves: Detected by LIGO in 2015.
✔ Black Hole Imaging: The 2019 Event Horizon Telescope image of a black hole.
Summary in Simple Terms:
🌍 Gravity is not a force but the bending of spacetime! The more massive an object, the more it curves spacetime, affecting the motion of everything around it.