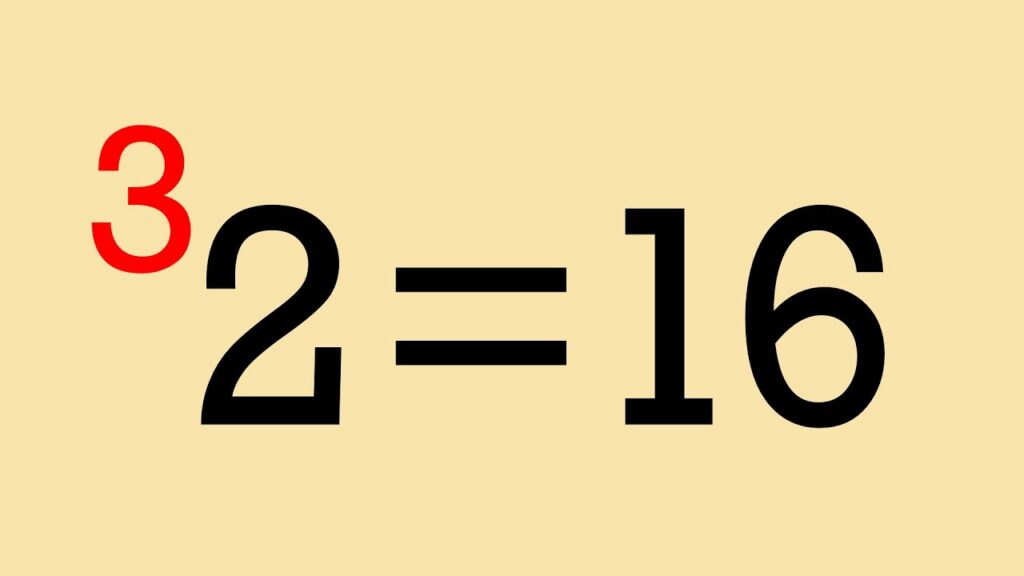Proposed by Albert Einstein in 1905, the Theory of Special Relativity revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and motion. It applies to objects moving at constant velocity (inertial frames) and is based on two fundamental postulates.
Einstein’s Two Postulates:
The Principle of Relativity:
- The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference (non-accelerating observers).
- No experiment can determine whether an observer is at rest or in uniform motion.
The Constancy of the Speed of Light:
- The speed of light (c≈3.0×10^8 m/s) is the same for all observers, regardless of their motion relative to the light source.
- Unlike sound or mechanical waves, light does not require a medium to travel.
Key Consequences of Special Relativity:
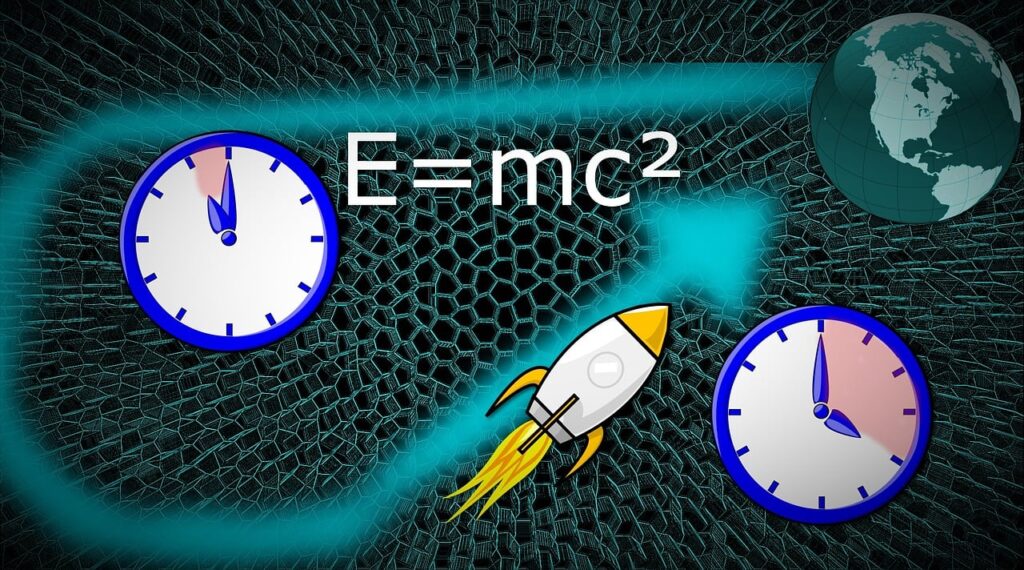
Time Dilation (Slowing of Time):
- Moving clocks run slower compared to stationary clocks.
- Formula:
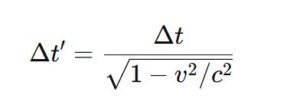
- Example: A fast-moving astronaut ages slower than people on Earth.
Length Contraction (Objects Shrink in Motion):
- Moving objects appear shorter along the direction of motion.
- Formula:
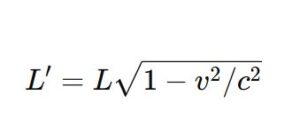
- Example: A spaceship moving at near-light speed appears shorter to an external observer.
Relativity of Simultaneity:
- Events that appear simultaneous to one observer may not be simultaneous to another moving observer.
Mass-Energy Equivalence:
- Einstein’s famous equation: E = mc^2
- Mass and energy are interchangeable; a small amount of mass can produce enormous energy (basis of nuclear energy and atomic bombs).
Experimental Proofs of Special Relativity:
✔ Particle accelerators: High-speed particles decay slower than expected, proving time dilation.
✔ GPS Systems: Time correction is needed due to relativistic effects.
✔ Muon decay: Muons from cosmic rays reach Earth in greater numbers than expected due to time dilation.
Summary in Simple Terms:
🚀 Moving faster changes how time, space, and mass behave. At near-light speeds, clocks slow down, objects shrink, and mass increases. Everything is relative, except for the speed of light!