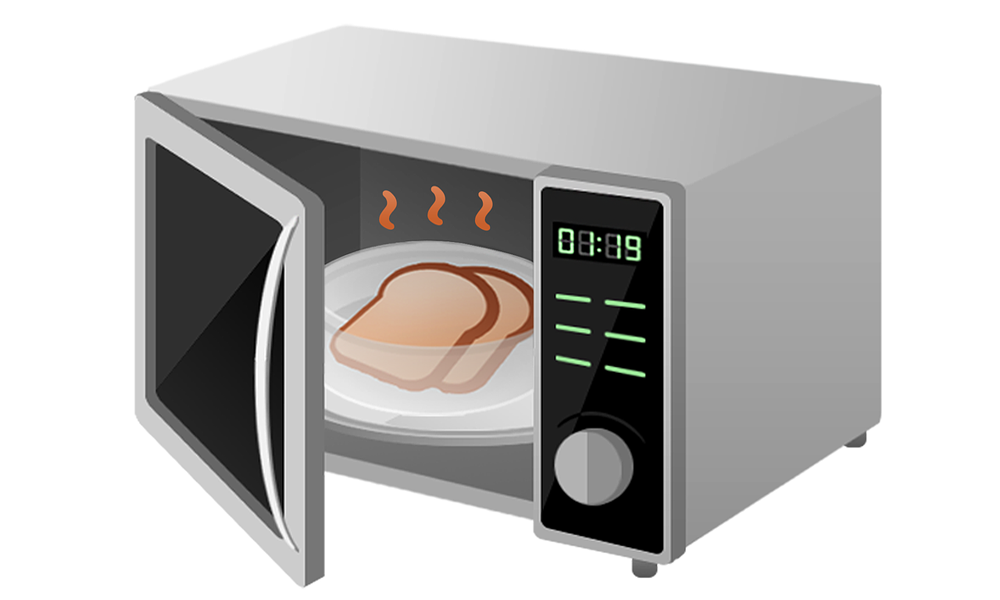
Microwaves heat food using a fascinating process that involves electromagnetic radiation. Here’s a simple explanation of how it works:
How Microwaves Heat Food
Microwave Radiation:
A microwave oven generates microwaves, which are a type of electromagnetic wave (similar to radio waves but with higher energy).
These microwaves are produced by a component called a magnetron.
Targeting Water Molecules:
Microwaves are specifically tuned to interact with water molecules (and to a lesser extent, fats and sugars) in food.
Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a positive end and a negative end. This makes them sensitive to electromagnetic fields.
Molecular Vibration:
When microwaves pass through food, they cause the water molecules to vibrate rapidly as they try to align with the alternating electric field of the microwaves.
This vibration creates friction between the molecules, which generates heat.
Even Heating:
The microwaves penetrate the food, heating it from the inside out (unlike conventional ovens, which heat from the outside in).
The turntable in the microwave helps distribute the microwaves evenly, ensuring more uniform heating.
Speed and Efficiency:
Because microwaves directly target the molecules in the food, they heat food much faster than traditional methods like stovetops or ovens.
Why Microwaves Don’t Heat All Materials
Microwaves primarily interact with polar molecules like water, fats, and sugars. Materials like glass, ceramic, or certain plastics don’t absorb microwaves well, which is why they stay cool (unless heated indirectly by the food).
Metals, on the other hand, reflect microwaves and can cause sparks or damage to the microwave, which is why metal containers are a no-go.
Fun Fact:
The microwave oven was invented by accident in 1945 by Percy Spencer, an engineer working on radar technology. He noticed that a chocolate bar in his pocket melted when exposed to microwaves, leading to the development of the first microwave oven!
This process is a great example of how science and technology come together to make our lives easier. If you’re writing a blog post, you could title it something like:
“How Do Microwaves Work? The Science Behind Quick and Easy Cooking!” 😊