What is Quantum Entanglement?
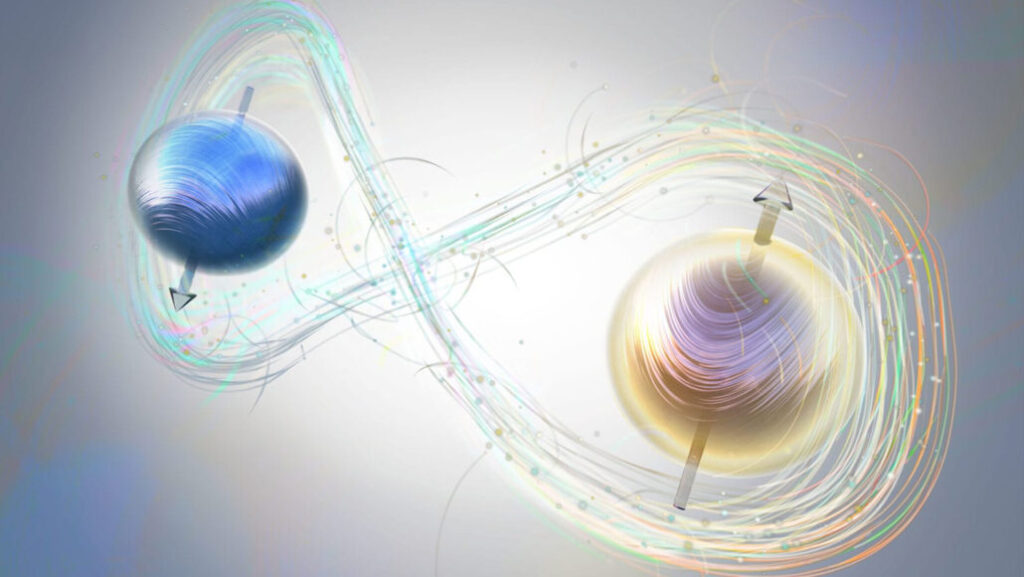
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon in quantum mechanics where two or more particles become interconnected in such a way that the state of one particle instantaneously affects the state of the other, regardless of the distance between them.
This means that if two particles are entangled, measuring the property (such as spin, polarization, or momentum) of one particle will immediately determine the corresponding property of the other particle, even if they are light-years apart.
How Does Quantum Entanglement Work?
Entanglement Formation:
- Two particles (e.g., electrons or photons) interact in a way that links their quantum states.
- This could happen naturally or be induced in a laboratory setting.
Separation of Particles:
- Once entangled, the particles can be physically separated by large distances.
Measurement Effect:
- If an observer measures a property (like spin) of one entangled particle, the corresponding property of the other particle is instantly determined, no matter how far apart they are.
Einstein’s “Spooky Action at a Distance”
Albert Einstein famously called quantum entanglement “spooky action at a distance”, as it seemed to contradict classical physics and the idea that information cannot travel faster than the speed of light.
However, experiments (such as the Bell test experiments) have confirmed that entanglement is real and does not violate relativity since no classical information is transmitted instantaneously.
Key Properties of Quantum Entanglement:
✔ Non-locality: Changes in one entangled particle are correlated with changes in the other, even at a distance.
✔ Instantaneous Correlation: The measurement of one particle instantly affects its entangled counterpart.
✔ No Classical Communication: No actual information is being sent faster than light—just correlated results.
Applications of Quantum Entanglement:
- Quantum Computing: Entanglement enables quantum computers to process information exponentially faster than classical computers.
- Quantum Cryptography (QKD): Secure communication using entanglement ensures that eavesdropping is impossible.
- Teleportation of Information: Quantum teleportation allows information to be transferred between entangled particles over long distances.
- Fundamental Physics Research: Entanglement is central to understanding quantum mechanics, black holes, and the nature of reality.
Does Entanglement Violate Relativity?
No! While entanglement correlations are instantaneous, actual information transfer still follows the speed of light limit, so it does not violate Einstein’s theory of relativity.
In Simple Terms:
🔹 Imagine two magic dice that always roll the same number, no matter how far apart they are. That’s quantum entanglement! 🎲🔗🎲
Would you like a deeper explanation on any specific aspect? 🚀